The dynamics of pricing is extremely important to understand, before you start raising or lowering the price of your product or service. Pricing is a powerful tool, perhaps the most powerful tool that will have direct impact on you position in the market, the demand of your product or service and not at least your financials. Yet working with pricing can be relatively complex, more complex than you immediately might think, hence it is important to think things through before proceeding with realizing your price changes.
Impact on demand is one important aspect to consider, but there are other
In this brief post we will only be covering the fundamental dynamics of pricing: the price changes impact on the demand for your product or service. Or rather the impact on demand your planned price change need to have in order for you to proceed with your plans, i.e. what you need to believe in before executing on your plans.
There are of course other aspects that you might want to consider before proceeding with your price changes, e.g. impact on brand, channel implications, implication on competitors etc.
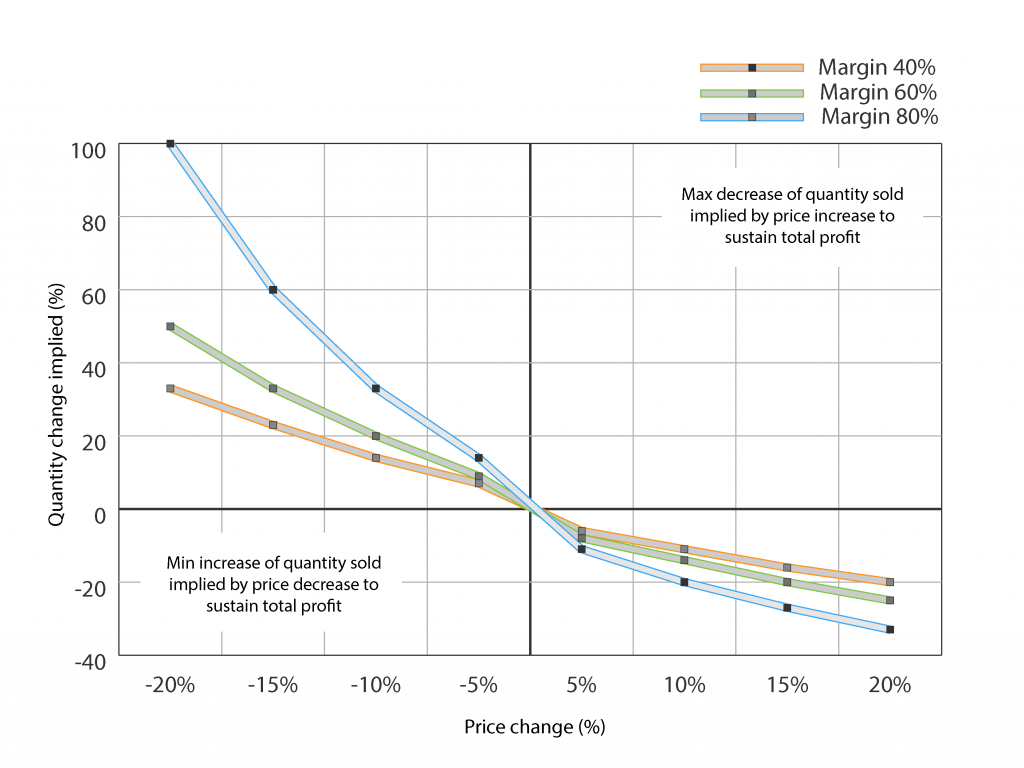
This is what you need to believe in if you are considering a price increase
Table describe how much quantity sold of your product/service need to increase in order to reach break-even on contributed profit given the profit margin of your product / service. This means as an example, in order to motivate a 10% price reduction for a product with 60% margin you need to believe that quantity sold will increase with at least 20%.
| Price decrease | -5% | -10% | -15% | -20% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | 33% | 100% | 300% | N/A |
| 40% | 14% | 33% | 60% | 100% |
| 60% | 9% | 20% | 33% | 50% |
| 80% | 7% | 14% | 23% | 33% |
This is what you need to believe in if you are considering a price decrease
Table show the maximum reduction in sold quantity that you can afford in order to sustain same total profit from a product/service when increasing its price. As an example, in order to motivate a 10% increase of a product with 60% margin you need to believe that quantity sold is reduced with less that 14%, otherwise price increase is not motivated.
| Price increase | +5% | +10% | +15% | +20% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | -20% | -33% | -43% | -50% |
| 40% | -11% | -20% | -27% | -33% |
| 60% | -8% | -14% | -20% | -25% |
| 80% | -6% | -11% | -16% | -20% |
Of course, implementing price changes of 5% or more perhaps seems drastic, but levels have been chosen just to demonstrate the dynamics in this. The key learning from this is that you need to factor in the margin of your product / service before starting to model on price changes and that you need to carefully consider the possible impact of demand from your price changes. In reality this means that you need to have a clear view on the demand curve for your specific product/service, otherwise estimating impact of the the price change will become a guesswork.
Make sure that you have modelled the price change thoroughly, carefully considering impact on demand in order to make sure you reach the effect you are looking for. Remember that changing price is a very powerful tool with direct impact on your business, and consequently it is a tool that you carefully need to model and analyse before you leverage it. Also, remember that apart from possible impact on demand, changes in your pricing might come with other impact as well, just as an example see below for the most obvious ones:
A. Brand
Changing your price might change your customers perception of your brand. You need to ask yourself if you can fit the new price in to your existing brand or whether it actually will lead to a re-positioning in the market.
B. Channel
Changing your price might change dynamics in your channel, a retailer might chose to stop ranging your product after a price decrease since that part of the portfolio is already filled with other brands; or the other way around of course.
C. Customer expectations
Price is typically having a significant impact on the customers expectations. This means that if you for instance manage to increase the price of your product your customers might as a consequence also expect a better quality of your product and/or better customer service and support.

Leave A Comment